University of Bristol and UKAEA team produce world's first carbon-14 diamond battery
Courtesy UKAEA
This new type of battery has the potential to power devices for thousands of years, making it an incredibly long-lasting energy source.
The battery leverages the radioactive isotope, carbon-14, known for its use in radiocarbon dating, to produce a diamond battery.
Several game-changing applications are possible. Bio-compatible diamond batteries can be used in medical devices like ocular implants, hearing aids and pacemakers, minimising the need for replacements and distress to patients.
Diamond batteries could also be used in extreme environments – both in space and on earth – where it is not practical to replace conventional batteries. The batteries could power active radio frequency (RF) tags where there is a need to identify and track devices either on earth or in space, such as spacecraft or payloads, for decades at a time, thus reducing costs and extending operational lifespan.

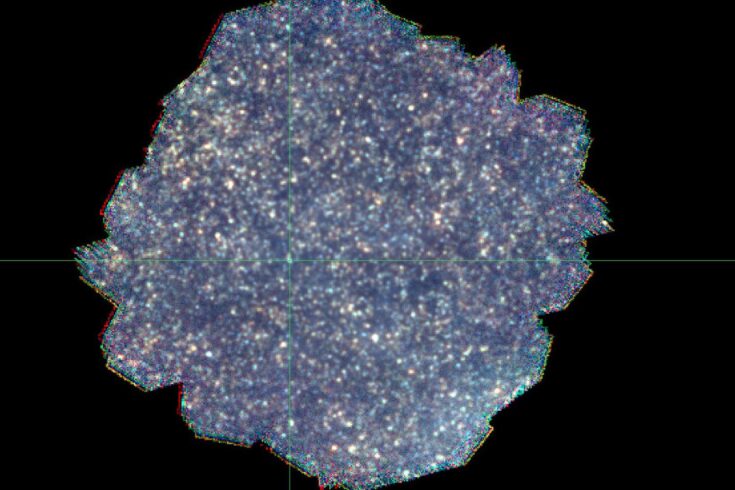
Above: Weak radio luminescence captured by a low light intensity camera from a synthetic diamond carbon film made from beta-emitting carbon-14 atoms.
Courtesy University of Bristol
Professor Tom Scott, Professor in Materials at the University of Bristol, said: “Our micropower technology can support a whole range of important applications from space technologies and security devices through to medical implants. We're excited to be able to explore all of these possibilities, working with partners in industry and research, over the next few years.”
The carbon-14 diamond battery works by using the radioactive decay of carbon-14, which has a half-life of 5,700 years, to generate low levels of power. It functions similarly to solar panels, which convert light into electricity, but instead of using light particles (photons), they capture fast-moving electrons from within the diamond structure.
“Diamond batteries offer a safe, sustainable way to provide continuous microwatt levels of power. They are an emerging technology that use a manufactured diamond to safely encase small amounts of carbon-14,” said Sarah Clark, Director of Tritium Fuel Cycle at UKAEA.

Above: Members of the Diamond Battery team, including Neil Fox, Professor of Materials for Energy at the University of Bristol (far left), with the Plasma Deposition Rig at UKAEA.
Courtesy University of Bristol / Credit UKAEA
A team of scientists and engineers from both organisations worked together to build a plasma deposition rig, a specialised apparatus used for growing the diamond at UKAEA’s Culham Campus.
This development is the result, in part, of UKAEA’s work on fusion energy.
The expertise gained in fusion research is helping to accelerate innovation in related technologies.