SSTL delivers first FOC payload for Galileo

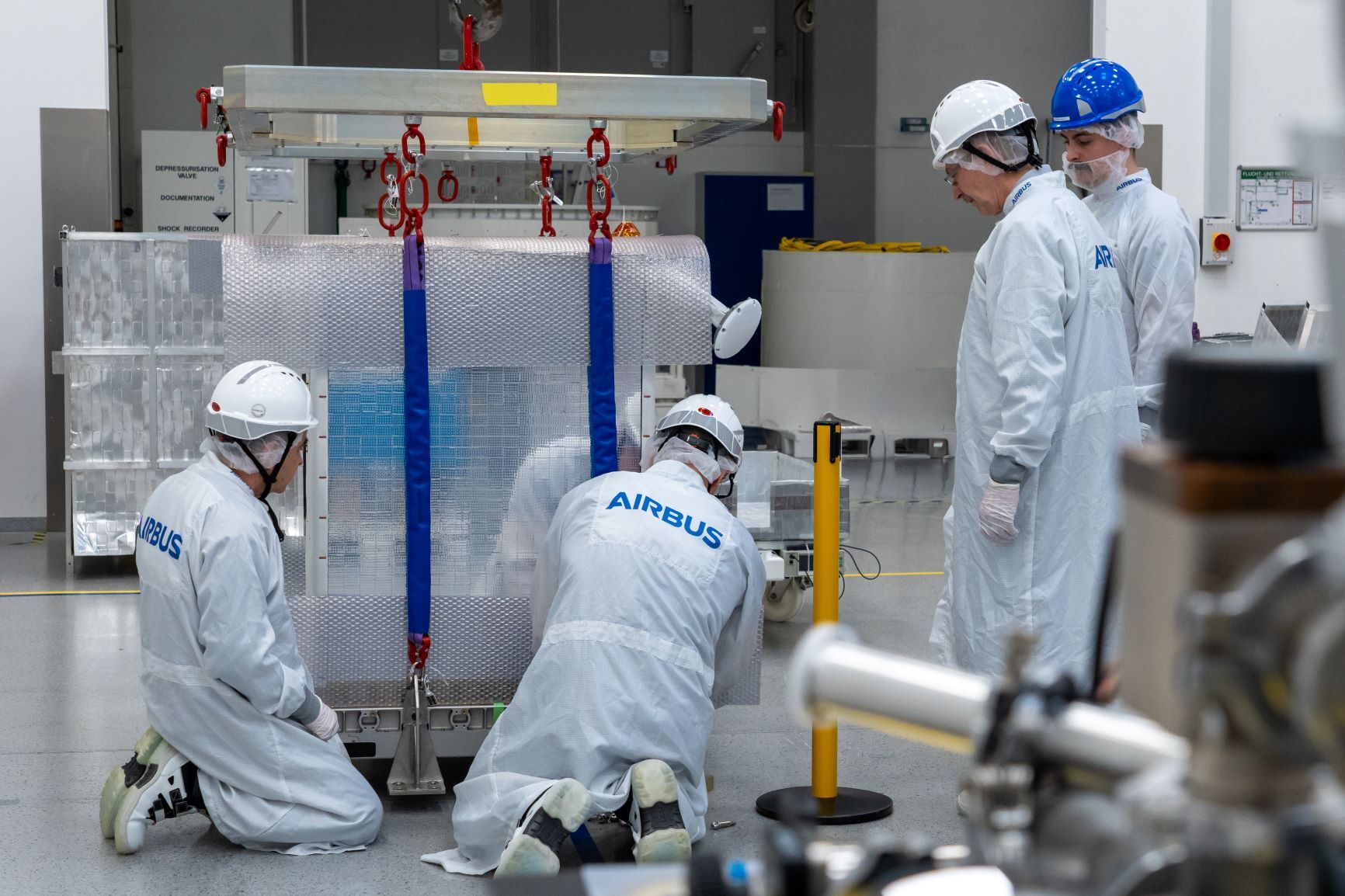
Above: Galileo FOC FM1 payload: The FOC FM1 payload laid out in SSTL's cleanroom for final tests before being boxed up for delivery to OHB (April 2012). The rubidium atomic clocks and hydrogen maser units can be seen centre left and right. Courtesy SSTL
As payload prime, SSTL is tasked with the development, assembly, integration and test (AIT) of the navigation payloads at their technical facility in Guildford, Surrey. This first payload has been shipped to prime contractor OHB in Bremen, Germany, for mechanical integration of the payload to platform and commencement of satellite AIT. A team of SSTL engineers will travel to Bremen to assist with the integration of the payload.
SSTL's payload solution will provide all of Galileo’s services, and is based on European-sourced atomic clocks, navigation signal generators, high power travelling wave tube amplifiers and antennas.
Dr Matt Perkins, SSTL CEO, commented “The delivery of our first Galileo payload is an important milestone towards achieving full satellite qualification at the end of the year, bringing together expertise, knowledge and innovation from almost a decade of SSTL involvement in Galileo. We are proud to lead the payload development for this landmark programme that will redefine what we expect from global navigation services”.
“The payload for the fifth satellite in the Galileo constellation is ready,” said Didier Faivre, ESA’s Director of the Galileo Programme and Navigation-related Activities.
“While the next two satellites to be launched are currently undergoing testing, the next ones are being built. Another important step forward for the programme was made today.”
In addition to these first fourteen, the OHB-SSTL consortium was awarded the contract to build a further eight satellites for the Galileo system by the European Space Agency (ESA) in February this year.
Galileo is Europe’s own Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS), providing real-time positioning, navigation and timing services with unrivalled accuracy and integrity. It will be interoperable with the American GPS system and Russia’s GLONASS system.