DESI 3D map of Universe one of TIME’s best inventions of 2024
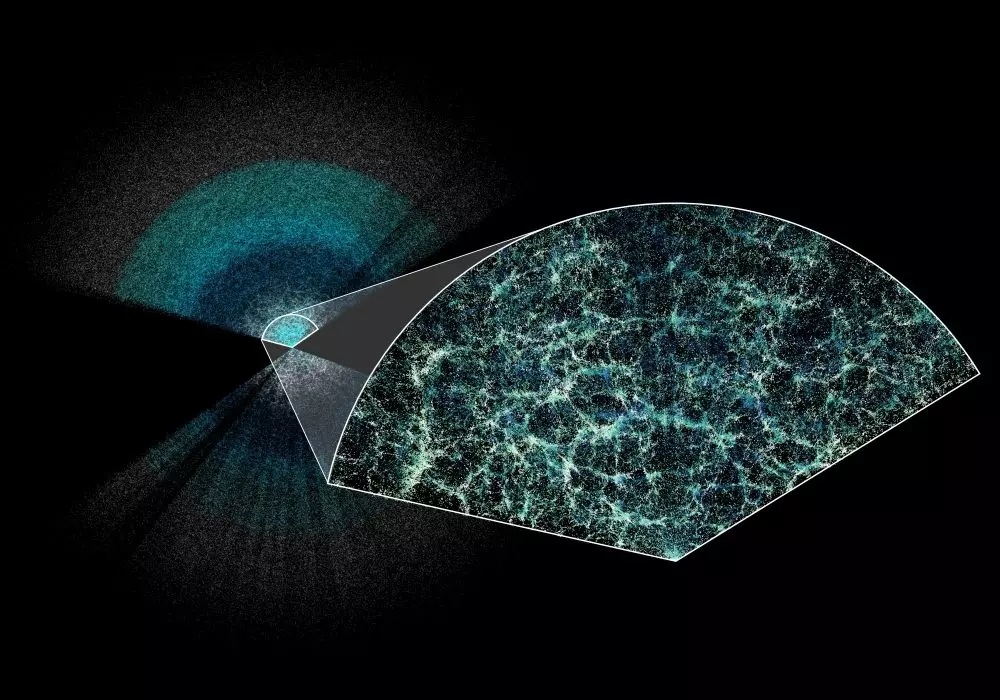

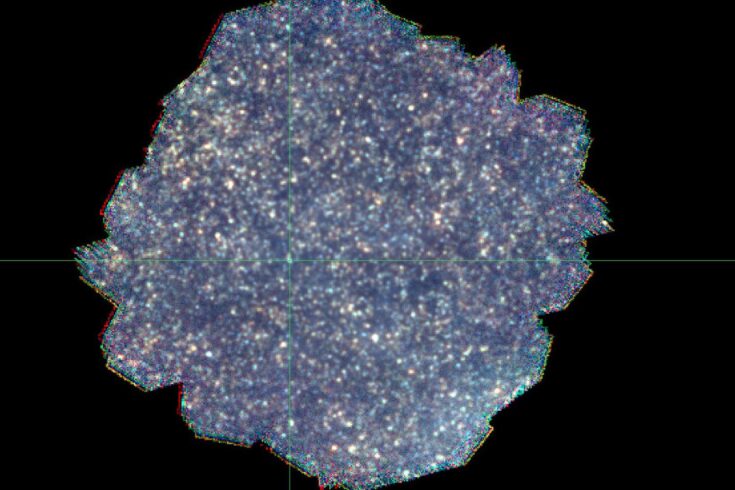
Above: DESI has made the largest 3D map of our universe to date. Earth is at the centre of this thin slice of the full map. In the magnified section, it is easy to see the underlying structure of matter in our Universe.
Courtesy University of Portsmouth / Credit: Claire Lamman/DESI collaboration; custom colormap package by cmastro
The international Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) project has led to the most precise measurement of our expanding universe. A team of international researchers, including scientists from the University of Portsmouth, mapped millions of galaxies and quasars with unprecedented detail, creating the biggest ever 3D map of the Universe and measuring how fast it has expanded over 11 billion years.
The annual list which features 200 extraordinary innovations changing people’s lives was revealed by TIME yesterday. To compile this year's list, TIME solicited nominations from TIME editors and correspondents around the world and through an online application process, paying special attention to growing fields—such as health care, AI, and green energy. TIME then evaluated each contender on a number of key factors, including originality, efficacy, ambition and impact.
DESI enabled researchers to create a map and measure the effects of dark energy, the mysterious cause of the Universe’s accelerating expansion.
DESI uses 5,000 tiny robots mounted within a mountaintop telescope, near Tucson, Arizona. By harnessing light from far-flung objects in space, DESI’s scientists mapped the cosmos as it was in its youth and traced its growth to what we see today.
This is the first-time scientists have measured the expansion history of the young Universe with a precision better than 1%, giving the best view yet of how the Universe has evolved.
Dr Seshadri Nadathur from the Institute of Cosmology and Gravitation at the University of Portsmouth, led parts of the analysis. He said: “The data we have acquired in just one year of operations is breathtaking – a map of the positions of nearly six million galaxies and quasars, measured to exquisite precision, from which we are able to tease out secrets of how the Universe has been expanding over the last 11 billion years.
“What’s even more exciting is that the results we have got so far seem to be hinting that our understanding of how dark energy behaves might have been wrong. There’s nothing scientists like better than discovering that they might have been wrong about something! But the evidence isn’t conclusive yet, so we need to be cautious – luckily we’ve got another four years of more data to come, which will help us find out one way or the other.”
Of the new list, TIME’s editors said: “The result is a list of 200 groundbreaking inventions, including the world's largest computer chip, a humanoid robot joining the workforce and a bioluminescent houseplant, that are changing how we live, work, play, and think about what’s possible.”
DESI is managed by the US Department of Energy’s (DOE) Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab). It includes the University of Portsmouth, Durham University and UCL and the University of Portsmouth, along with individual researchers at the universities of Cambridge, Edinburgh, St Andrews, Sussex and Warwick from the UK.
See the full list here: time.com/best-inventions-2024